

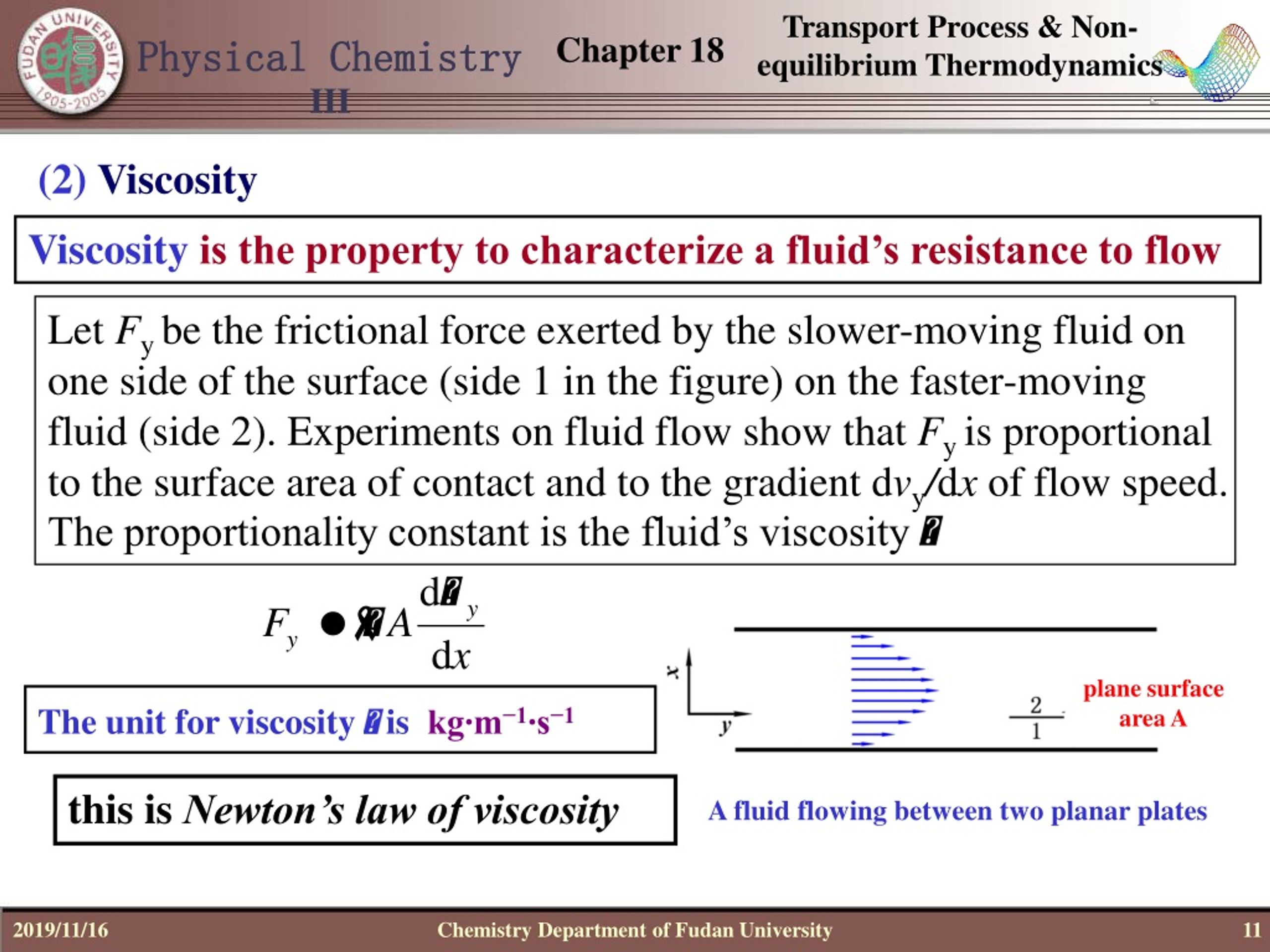
The value of either can be derived as a function of temperature or as a given value (i.e. Introduction: Friction at the Molecular Level Viscosity is, essentially, fluid friction. It is the name given to internal friction that exists between the layers of the molecules of fluids (liquid or gas) in contact with surfaces. It is the property of a liquid that opposes the relative motion between different layers. The viscosity of a particular fluid is how easily it flows. Viscosity Definition: We can define viscosity as the internal friction between layers of a liquid or gas in motion. The inverse of η is also known as fluidity, φ. Viscosity is a measure of flowability at particular temperatures. Viscoelasticity calculations depend heavily on the viscosity variable, η. Viscoelasticity was further examined in the late twentieth century when synthetic polymers were engineered and used in a variety of applications. You can think of water (low viscosity) and honey (high viscosity). In the nineteenth century, physicists such as Maxwell, Boltzmann, and Kelvin researched and experimented with creep and recovery of glasses, metals, and rubbers. Viscosity is often referred to as the thickness of a fluid. Whereas elasticity is usually the result of bond stretching along crystallographic planes in an ordered solid, viscosity is the result of the diffusion of atoms or molecules inside an amorphous material. Viscoelastic materials have elements of both of these properties and, as such, exhibit time-dependent strain. Elastic materials strain when stretched and immediately return to their original state once the stress is removed. Shear stress is the the friction between fluid particles sliding past each other.

Viscosity is denoted by (eta) as the ratio of the shear stress (Force/Area) to the strain rate. Viscous forces oppose the motion of one portion of the fluid relative to another.

Poiseuille’s law for flow in a tube is Q (P2 P1)r4 8l. Explanation: Viscosity is internal friction inside a fluid. For laminar flow in a tube, Poiseuille’s law for resistance states that R 8l r4. Flow is proportional to pressure difference and inversely proportional to resistance: Q P2 P1 R. Stokes' law makes the following assumptions for the behavior of a particle in a fluid: Laminar flow Spherical particles Homogeneous (uniform in composition) material Smooth surfaces Particles do not interfere with each other.
The amount of water in clouds is enormous. Viscous materials, like water, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Viscosity has units of (N / m2) s or Pa s. v is the flow velocity relative to the object (meters per second). Stokes Law formula is a mathematical expression for the drag force that prevents tiny spherical particles from falling through a fluid medium. Viscosity 1 Viscosity Viscosity Clear liquid above has lower viscosity than the substance below SI symbol:, SI unit: Pas kg/(sm) Derivations from other quantities: Gt Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear stress or tensile stress.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
